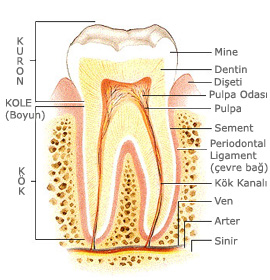
It is a branch of dentistry that aims to treat the caries that occur in the outer layers of the tooth such as enamel or dentin in the early period and thus to prevent the progression of caries and to protect the vitality of the tooth. Thanks to this, the next stages, endodontics (root canal treatment) or tooth extraction, are prevented. The tooth material losses that occur are treated with aesthetic, functional and compatible filling of the oral tissues.
Bacteria plaque formed by bacteria in the mouth can form acid from the mouth residues of sugary and floury foods. These acids dissolve the mineral tissue of the teeth, causing the enamel of the tooth to deteriorate and ultimately the start of tooth decay.
The area to be applied in the selection of the type of filling to be applied to the patient, the chewing forces effective in this area, the patient’s aesthetic expectations and the amount of material loss are of great importance.
Types of fillings
1. Amalgam Fillings (Metal Fillings)
It has been the most preferred filling material for years with its durability and economical nature. Nowadays, increasing aesthetic demands of patients, rumors about the effects of mercury contained in amalgam on human health and adhesive systems (tooth-colored fillings) cause this material to be abandoned gradually.
In addition, some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to the materials contained in amalgam. In fact, the amount of mercury released in the mouth as a result of chewing and grinding is much smaller than the amount taken in water, air and food. It has been concluded with all scientific studies that mercury is harmless. Although it is rare, people with different metal restorations in the mouth environment or when another metal such as a fork enters the mouth environment may have sensitivity arising from electrification. . It is prepared by mixing the powder consisting of 70% silver, 23% tin, a small amount of copper and zinc with mercury. The mixture is piled into the cavity prepared by the dentist and the filling hardens in a few hours. The area where the amalgam filling is made should not use at least one hour; In the following 24 hours, care should be taken not to chew hard things in that area. After 24 hours, the patient should be given a second appointment for polishing. The polishing process will reduce corrosion by obtaining a smooth surface. As with every filling application, after amalgam fillings, there may be hot-cold sensitivity for a short time.
2. Composite Resins (Tooth Color Fillings, Aesthetic Fillings, Adhesive Systems)
They are the preferred tooth-colored restorations, especially in cases where aesthetics are at the forefront. Due to its connection properties with teeth, there is no need to remove material from the tooth in order to provide retention as in amalgam fillings; it is only sufficient to remove the caries. Composite fillings are placed in the prepared cavity layer by layer and each layer is cured with a special light. When this process is finished, composite fillings are shaped and corrected according to the tooth.
Composites can be used not only to restore caries, but also for their cosmetic effects by changing the color and shape of teeth. The most important disadvantages are the sensitivity for a period of time after the procedure. The colors of the fillings may change slightly with coloring foods such as coffee and tea.
Unlike amalgam restorations, composite fillings are completed in one session. After treatment, the patient can use his / her tongue normally. The most important disadvantages are the sensitivity for a period of time after the procedure.
3.Inlays and Onlays
Root canal treatment is a kind of partial crown prosthesis that restores the loss of material in the teeth due to factors such as caries and trauma to complement only the missing parts of the tooth, or a kind of filling prepared from gold, various alloys, composite or porcelain in the laboratory.
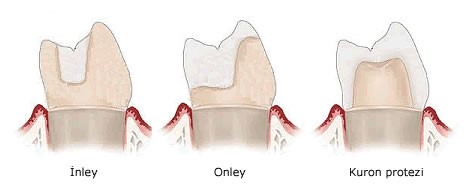
In inlays and onlays, as in laminate veneers, the solid part of the tooth is protected in its natural state. It is preferred to replace metallic and dark colored amalgam restorations in the posterior teeth of patients with high esthetic and comfort expectations. In addition, when a large number of fillings are required, the porcelain fillings prepared in the laboratory are placed in the second session, following the tooth preparation and impression taking in one session, saving time. Likewise, the preparation of restorations in the laboratory, not in the mouth, like conventional fillings, provides a perfect harmony.
Unlike the mercury in amalgam, porcelain is one of the most biologically compatible materials with the human body. In addition, its high aesthetic properties make it a reason to prefer porcelain. Due to all these factors, the use of metal alloys and composites has decreased considerably today and has been replaced by porcelain inlays.
